Suggested Textbook The Practice of Statistics for AP Daren S. Starnes, Daniel S. Yates, David S. Moore 4th Edition Find All Video Solutions for Your Textbook Question Solved step-by-step The prior probabilities for events A1 and A2 are P (A1) = 0.40 and P (A2) = 0.55. It is also known that P (A1 ∩ A2) = 0.
Solved = = The prior probabilities for events A1 and A2 are | Chegg.com
question 2 people found it helpful jacob193 Answer: (a) and are indeed mutually-exclusive. (b) , whereas . (c) . (d) , whereas Step-by-step explanation: (a) means that it is impossible for events and to happen at the same time. Therefore, event and are mutually-exclusive. (b) By the definition of conditional probability: . Rearrange to obtain: .

Source Image: transtutors.com
Download Image
If events A and B are independent, then the probability of simultaneous occurrence of event A and event B can be found with: (blank). Assume P(C) = 0.2, P(D = 0.6, and P(C(D)) = 0.1. Find the probability that D does not happen given that C happens.

Source Image: flugschule-pinzgau.at
Download Image
Solved The prior probabilities for events A1 and A2 are | Chegg.com Sep 7, 2023answer answered The prior probabilities for events A1 and A2 are P (A1)=0.40 and P (A2)=0.60. It is also known that P (AINA2)= 0. Suppose P (B|A1)=0.10 and P (B|A2)=0.08. Answer the following questions. (a) Are Ai and A2 are mutually exclusive? Explain. (b) Calculate P (AINB) and P (A2nB). (c) Calculate P (B).

Source Image: scribd.com
Download Image
The Prior Probabilities For Events A1 And A2 Are
Sep 7, 2023answer answered The prior probabilities for events A1 and A2 are P (A1)=0.40 and P (A2)=0.60. It is also known that P (AINA2)= 0. Suppose P (B|A1)=0.10 and P (B|A2)=0.08. Answer the following questions. (a) Are Ai and A2 are mutually exclusive? Explain. (b) Calculate P (AINB) and P (A2nB). (c) Calculate P (B). monsterking690 04/28/2020 Mathematics College answered • expert verified The prior probabilities for events A1 and A2 are P (A1) = 0.30 and P (A2) = 0.55. It is also known that P (A1 ∩ A2) = 0. Suppose P (B | A1) = 0.20 and P (B | A2) = 0.05. If needed, round your answers to three decimal digits.a) Are A1 and A2 mutually exclusive?
Fundamentals of Business Statistics: 6E John Loucks | PDF | Probability | Experiment
Sep 8, 2023Next, we also have P A1 intersection A2 is 0. Next, we also have P of B given A1 is 0 .2, P of B given A2 is 0 .05. For the first part of the problem, we want to check whether A1 and A2 are mutually exclusive. So, note that P of A1 union A2 can be written as P of A1 plus P of A2 minus P of A1 intersection A2. Now, this value is given as 0. So Solved The prior probabilities for events A1,A2, and A3 are | Chegg.com

Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
The prior probabilities for events $A _ 1 , A _ 2 ,$ | Quizlet Sep 8, 2023Next, we also have P A1 intersection A2 is 0. Next, we also have P of B given A1 is 0 .2, P of B given A2 is 0 .05. For the first part of the problem, we want to check whether A1 and A2 are mutually exclusive. So, note that P of A1 union A2 can be written as P of A1 plus P of A2 minus P of A1 intersection A2. Now, this value is given as 0. So
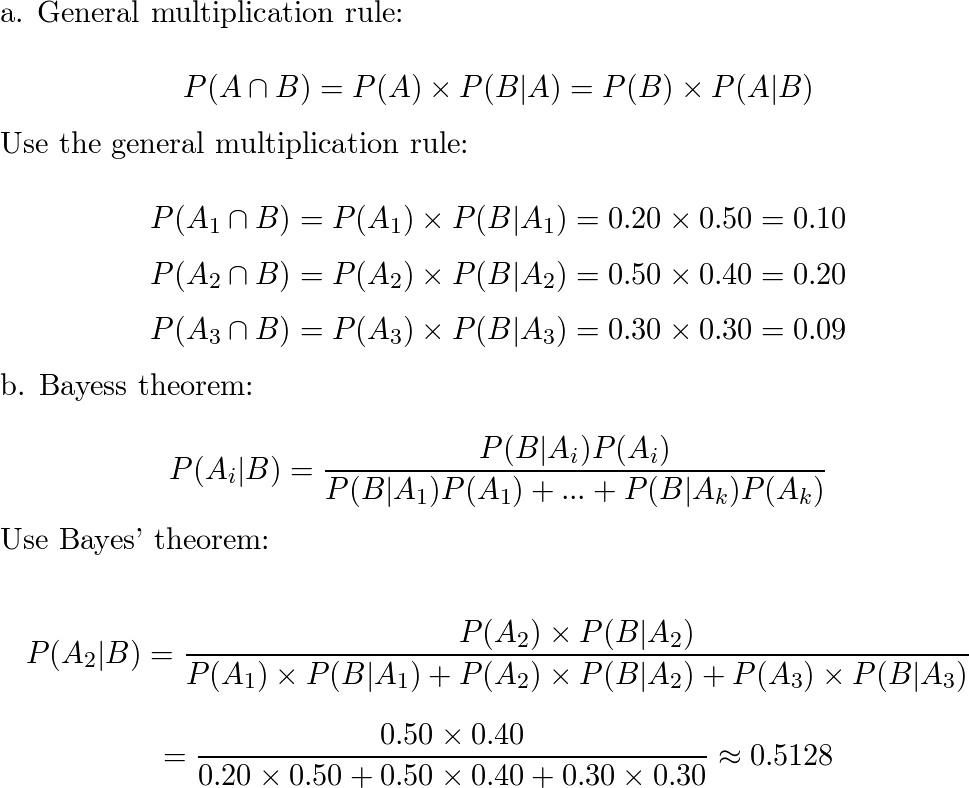
Source Image: quizlet.com
Download Image
Solved = = The prior probabilities for events A1 and A2 are | Chegg.com Suggested Textbook The Practice of Statistics for AP Daren S. Starnes, Daniel S. Yates, David S. Moore 4th Edition Find All Video Solutions for Your Textbook Question Solved step-by-step The prior probabilities for events A1 and A2 are P (A1) = 0.40 and P (A2) = 0.55. It is also known that P (A1 ∩ A2) = 0.

Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Solved The prior probabilities for events A1 and A2 are | Chegg.com If events A and B are independent, then the probability of simultaneous occurrence of event A and event B can be found with: (blank). Assume P(C) = 0.2, P(D = 0.6, and P(C(D)) = 0.1. Find the probability that D does not happen given that C happens.

Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Cambridge Assessment International Education Catalogue 2018 by Cambridge International Education – Issuu Math Statistics and Probability Statistics and Probability questions and answers The prior probabilities for events A1 and A2 are P (A1 ) = 0.30 and P (A2 ) = 0.70. It is also known that P (A1 ∩ A2 ) = 0. Suppose P (B | A1 ) = 0.20 and P (B | A2 ) = 0.05. If needed, round your answers to three decimal digits. Complete and answer parts B-D

Source Image: issuu.com
Download Image
Remote Sensing | Free Full-Text | Improved Spatiotemporal Information Fusion Approach Based on Bayesian Decision Theory for Land Cover Classification Sep 7, 2023answer answered The prior probabilities for events A1 and A2 are P (A1)=0.40 and P (A2)=0.60. It is also known that P (AINA2)= 0. Suppose P (B|A1)=0.10 and P (B|A2)=0.08. Answer the following questions. (a) Are Ai and A2 are mutually exclusive? Explain. (b) Calculate P (AINB) and P (A2nB). (c) Calculate P (B).

Source Image: mdpi.com
Download Image
The prior probabilities for events $A _ 1 $ and $A _ { 2 | Quizlet monsterking690 04/28/2020 Mathematics College answered • expert verified The prior probabilities for events A1 and A2 are P (A1) = 0.30 and P (A2) = 0.55. It is also known that P (A1 ∩ A2) = 0. Suppose P (B | A1) = 0.20 and P (B | A2) = 0.05. If needed, round your answers to three decimal digits.a) Are A1 and A2 mutually exclusive?

Source Image: quizlet.com
Download Image
The prior probabilities for events $A _ 1 , A _ 2 ,$ | Quizlet
The prior probabilities for events $A _ 1 $ and $A _ { 2 | Quizlet question 2 people found it helpful jacob193 Answer: (a) and are indeed mutually-exclusive. (b) , whereas . (c) . (d) , whereas Step-by-step explanation: (a) means that it is impossible for events and to happen at the same time. Therefore, event and are mutually-exclusive. (b) By the definition of conditional probability: . Rearrange to obtain: .
Solved The prior probabilities for events A1 and A2 are | Chegg.com Remote Sensing | Free Full-Text | Improved Spatiotemporal Information Fusion Approach Based on Bayesian Decision Theory for Land Cover Classification Math Statistics and Probability Statistics and Probability questions and answers The prior probabilities for events A1 and A2 are P (A1 ) = 0.30 and P (A2 ) = 0.70. It is also known that P (A1 ∩ A2 ) = 0. Suppose P (B | A1 ) = 0.20 and P (B | A2 ) = 0.05. If needed, round your answers to three decimal digits. Complete and answer parts B-D