Molecular structures. In their simplest form, carbohydrates can be represented by the stoichiometric formula (CH 2 O) n, where n is the number of carbons in the molecule. For simple carbohydrates, the ratio of carbon-to-hydrogen-to-oxygen in the molecule is 1:2:1. This formula also explains the origin of the term “carbohydrate“: the components are carbon (” carbo”) and the components
Macromolecules Definition, Types & Uses – Video & Lesson Transcript | Study. com
May 27, 20231. Erythrose It is a 4-carbon monomer, i.e., a tetrose sugar. 2. Threose It is also 4 carbon monomer similar to erythrose in structure with a small variation. Five-carbon carbohydrate monomers Ribose sugar It is a 5-carbon monomer. A pentose sugar with many isomers. It is found widely in the Coenzymes, ATP, NADH, nucleic acids of living organisms.
Source Image: byjus.com
Download Image
For example, a carbohydrate is a macromolecule that is classified as a polymer because it is made up of repeating monosaccharides, but a fat (lipid) is a macromolecule that cannot be further classified because if you look under the ‘monomers’ column, it is built up by more than one monomer. Hope this helped! 2 comments ( 114 votes) Show more
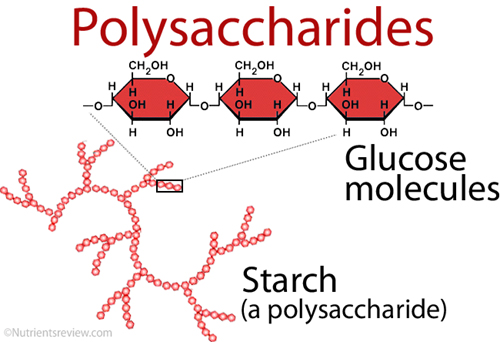
Source Image: theeducationjourney.com
Download Image
What are the functional in carbohydrates? All Subjects Chemistry Determining Molecular Formulas What is the monomer of carbohydrates? Q: What is the monomer of carbohydrates? What is the monomer of carbohydrates? Flexi Says: A monosaccharide, the monomer of carbohydrates, is a simple sugar such as fructose or glucose.
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
The Monomer Of A Carbohydrate Is Called
All Subjects Chemistry Determining Molecular Formulas What is the monomer of carbohydrates? Q: What is the monomer of carbohydrates? What is the monomer of carbohydrates? Flexi Says: A monosaccharide, the monomer of carbohydrates, is a simple sugar such as fructose or glucose. Carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldehydes, polyhydroxy ketones, or other compounds that hydrolyze to polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketones. The general formula of simple carbohydrates is CnH2nOn C n H 2 n O n, which can also be written as Cn ⋅ (H2O)n C n ⋅ ( H 2 O) n which is the origin of the name carbohydrates, i.e., hydrates of carbon.
Are carbohydrates and proteins also polymers like DNA and RNA? If so, how do they differ from them? – Quora
24.1: Names and Structures of Carbohydrates. classify a specific carbohydrate as being a monosaccharide, disaccharide, trisaccharide, etc., given the structure of the carbohydrate or sufficient information about its structure. classify a monosaccharide according to the number of carbon atoms present and whether it contains an aldehyde or ketone SOLVED: Fill in the following table: Does it have a Functions Macromolecule polymer Monomer in living Examples structure? cells (YIN) Carbohydrates monosaccharides (Carbohydrates polysaccharides Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids
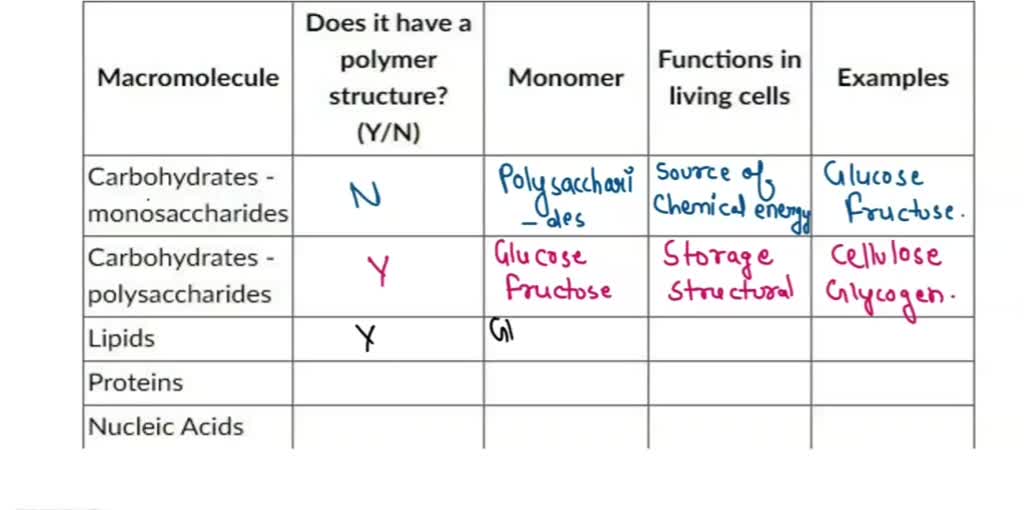
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
What are the monomers of carbohydrates? – Quora 24.1: Names and Structures of Carbohydrates. classify a specific carbohydrate as being a monosaccharide, disaccharide, trisaccharide, etc., given the structure of the carbohydrate or sufficient information about its structure. classify a monosaccharide according to the number of carbon atoms present and whether it contains an aldehyde or ketone
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
Macromolecules Definition, Types & Uses – Video & Lesson Transcript | Study. com Molecular structures. In their simplest form, carbohydrates can be represented by the stoichiometric formula (CH 2 O) n, where n is the number of carbons in the molecule. For simple carbohydrates, the ratio of carbon-to-hydrogen-to-oxygen in the molecule is 1:2:1. This formula also explains the origin of the term “carbohydrate“: the components are carbon (” carbo”) and the components

Source Image: study.com
Download Image
What are the functional in carbohydrates? For example, a carbohydrate is a macromolecule that is classified as a polymer because it is made up of repeating monosaccharides, but a fat (lipid) is a macromolecule that cannot be further classified because if you look under the ‘monomers’ column, it is built up by more than one monomer. Hope this helped! 2 comments ( 114 votes) Show more

Source Image: toppr.com
Download Image
Biology Ch. 2-3 “Carbohydrate Structure” Diagram | Quizlet Jan 2, 2024carbohydrate, class of naturally occurring compounds and derivatives formed from them. In the early part of the 19th century, substances such as wood, starch, and linen were found to be composed mainly of molecules containing atoms of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) and to have the general formula C 6 H 12 O 6; other organic molecules

Source Image: quizlet.com
Download Image
Current Status of Carbohydrates Information in the Protein Data Bank | Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling All Subjects Chemistry Determining Molecular Formulas What is the monomer of carbohydrates? Q: What is the monomer of carbohydrates? What is the monomer of carbohydrates? Flexi Says: A monosaccharide, the monomer of carbohydrates, is a simple sugar such as fructose or glucose.

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
SOLVED: Identify the following macromolecule, and circle and label the monomers: Carbohydrate (Disaccharide) H H CH2OH H OH H H HO OH CH2OH H OH OH H Carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldehydes, polyhydroxy ketones, or other compounds that hydrolyze to polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketones. The general formula of simple carbohydrates is CnH2nOn C n H 2 n O n, which can also be written as Cn ⋅ (H2O)n C n ⋅ ( H 2 O) n which is the origin of the name carbohydrates, i.e., hydrates of carbon.
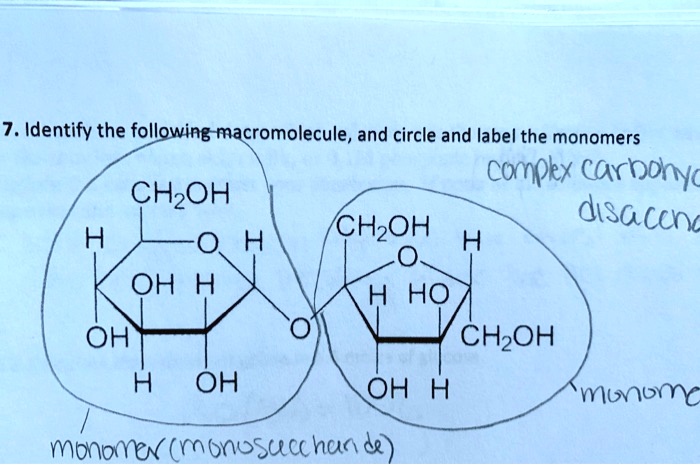
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
What are the monomers of carbohydrates? – Quora
SOLVED: Identify the following macromolecule, and circle and label the monomers: Carbohydrate (Disaccharide) H H CH2OH H OH H H HO OH CH2OH H OH OH H May 27, 20231. Erythrose It is a 4-carbon monomer, i.e., a tetrose sugar. 2. Threose It is also 4 carbon monomer similar to erythrose in structure with a small variation. Five-carbon carbohydrate monomers Ribose sugar It is a 5-carbon monomer. A pentose sugar with many isomers. It is found widely in the Coenzymes, ATP, NADH, nucleic acids of living organisms.
What are the functional in carbohydrates? Current Status of Carbohydrates Information in the Protein Data Bank | Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling Jan 2, 2024carbohydrate, class of naturally occurring compounds and derivatives formed from them. In the early part of the 19th century, substances such as wood, starch, and linen were found to be composed mainly of molecules containing atoms of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) and to have the general formula C 6 H 12 O 6; other organic molecules